
Digital Signatures and How to Use Them in PDFs with FineReader PDF 15
Excerpt: Digital signatures have become widely accepted and are accepted as valid and legally binding in many industries from government, healthcare, manufacturing, transportation, financial services, and others. Learn more about how secure they are and how to apply them using FineReader PDF 15.
About the author:

Contents
- 1 Digital Signatures and How to Use Them in PDFs with FineReader PDF 15
- 1.1 What is a digital signature?
- 1.2 Uses of digital signatures for documents
- 1.3 How secure are digital signatures?
- 1.4 Received a signed PDF, now how to check validity of the signature?
- 1.5 Have a PDF to sign? Here is how to create and add a digital signature
- 1.6 I want to sign documents digitally, but I don’t have a Certificate. How do I get private and public keys to create digital signatures?
- 1.7 What kinds of digital signatures are supported by FineReader PDF 15?
What is a digital signature?
Once people started to rely on digital document exchange, the need for a digital means to confirm and verify authenticity of the documents arose. A digital signature is an equivalent for digital documents, such as PDFs, of a wet-ink signature on paper documents. From a technology standpoint, a digital signature is a message encrypted by the signer using a secret private key, which associates itself with the document and the signer. This message can then be decrypted by anyone else with a matching public key for verification.
Uses of digital signatures for documents
A digital signature is a versatile method to sign documents in electronic form, which is used to provide the following:
- Authentication—a digital signature on a document authenticates the identity of the person who signed it
- Integrity—a valid digital signature on a document certifies that the document hasn’t been altered in transit from the one who signed it to the recipients
- Non-repudiation—the person who signed the document cannot deny having signed it at a later time
In many jurisdictions, digital signatures not only verify that the document is true and not altered, but also have legal authority, i.e., making documents such as contracts legally binding—in the same way as documents with traditional pen-on-paper signatures. For such circumstances, the EU passed the EU Directive for Electronic Signatures in 1999, and the United States passed the Electronic Signatures in Global and National Commerce Act (ESIGN) in 2000. Digital signatures are now widely accepted and used in government, healthcare, manufacturing, transportation, financial services, and other industries.
How secure are digital signatures?
Digital signatures are very reliable. They are based on modern encryption algorithms. Digital signatures are easy to verify at the recipient’s side thanks to encryption algorithms with public keys. They are very reliable and resistant to forgery or fraudulent actions thanks to Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) standardized services widely adopted to generate, distribute, and control public keys. In fact, digital signatures can be considered as even more reliable than wet-ink ones. Here are just a few reasons why:
- Although wet-ink signatures are very difficult to forge so that the imitation withstands professional scrutiny, such scrutiny requires expert work—while, in the case of a digital signature, anyone can easily and reliably verify it with software
- Also, while a wet-ink signature from one document can be imitated on another, every digital signature is unique to the document it is applied for, and therefore can’t be copied to another document
- A digital signature is applied to the entire document and any change to it inevitably invalidates the digital signature. With paper documents, though, it’s quite easy to substitute a page if the ink signature is applied just on the last page. Even if all the pages are individually signed with ink, still someone may try to forge its content (mechanically, chemically, etc.)—and the wet-ink signature just cannot “warn” anyone about that
Received a signed PDF, now how to check validity of the signature?
It’s really simple. Just open the PDF document in ABBYY FineReader PDF 15. Everything that is needed to validate the signature is inside the document, and the software will do it for you immediately. If the signature is valid, and there were no changes made to the document since it had been signed, FineReader PDF will show you a green “Valid” sign in the “Digital Signatures” pane:

If the signature isn’t valid, or the document has been edited, the status of the signature will be “Invalid”, and you shouldn’t trust that document:
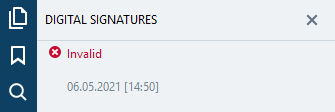
You can view properties of a signature using a command from the right-click menu, or by double-clicking on it in the “Digital Signatures” pane.
Have a PDF to sign? Here is how to create and add a digital signature
- To sign a document, click the Signature button
 on the main toolbar and choose “Add digital signature…” option.
on the main toolbar and choose “Add digital signature…” option. - Click and drag to select a rectangular area where you want to put the signature, or just click the desired location if you’re good with the default size. Then, “Add Digital Signature” dialogue window will appear.
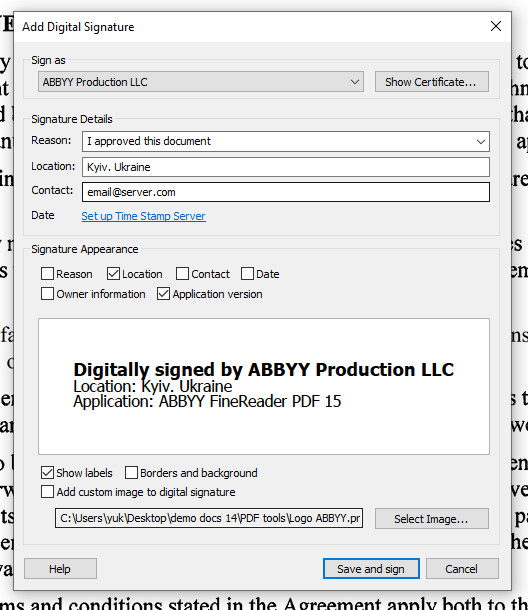
- In “Sign As” dropdown, choose the certificate you want to use to sign the document.
- Then you can indicate the “Reason” using the drop-down list to specify the reason for signing the document. You can add your own text. The Location and Contact fields are used to specify the location where the document was signed and your contact information respectively.
- Digital signatures contain information about date and time of signing. Special Time Stamp servers are used for providing such information for this purpose. In FineReader PDF 15, you can specify the URL of the Time Stamp server that is used by yourself or your organization. To do so, click “Set up Time Stamp Server”. Otherwise, just skip this step and FineReader PDF will use the default.
- Then, in the “Signature Appearance” section, you can adjust which information from the signature will be visible: reason, location, contact, date and time of signing, signature owner information, as well as the name and version number of the FineReader program that was used. To display information in the signature, without the field names, uncheck “Show labels”.
- Select the “Borders and background” option to add a border and a gray background to your signature, instead of a transparent background.
- You also have the option to add an image to the digital signature, such as a facsimile of your handwritten signature. To do that, select “Add custom image to digital signature” and choose the image file with the “Select Image…” button.
- Click “Save and sign”. You will be prompted to save the document as a separate signed copy.
I want to sign documents digitally, but I don’t have a Certificate. How do I get private and public keys to create digital signatures?
To be able to sign documents digitally, you first must prove your identity and get a Certificate and a pair of the unique electronic keys from one of the organizations called Certificate Authorities (CA). The keys are:
- Private key: Used for signing documents, and you keep it securely away from the reach of anybody else
- Public key: Used by others to verify your digital signatures, and it is provided in your Certificate issued by the CA
The Certificate is an electronic document that identifies you as a holder of a specific public key, which therefore enables you to be identified as a signer when someone gets a document with a digital signature made by you.
If you are an employee in an organization, it might be that you already have the certificate or can get it through your organization. If you aren’t sure, it is recommended that you check with the IT-service of your organization, and, if needed, they could also help you with installing it properly.
With FineReader PDF 15, you can put digital signatures on PDF documents using the certificates installed in Windows Certificate store—then they become available for signing documents. You can also use PIN-protected certificates usually stored on special cards (smartcards).
What kinds of digital signatures are supported by FineReader PDF 15?
FineReader PDF supports working with digital signatures based on modern, secure encryption algorithms SHA256, SHA384, SHA512, and MD5. If you have an old certificate based on SHA1 encryption, FineReader PDF will anyway use a secure SHA256 to apply a digital signature to your document.
The software also supports applying digital signatures using PIN-protected digital certificates (smartcards), which are typically stored on special cards read with a device connected to a computer.
A wide range of digital certificates are supported for validation and applying digital signatures, including long-term validation (LTV), such as DocuSign, and others. They are specially designed to provide the possibility to successfully validate signatures for many years ahead.
Learn more about digital signatures


